While experimenting with Apache Beam, I noticed there is a big difference in the performance of Java vs. Python SDK when reading from BigQuery. See this. So I thought it would be good to measure the performance of the Java vs. Python client libraries that ship with BQ. Let’s jump right in:
Java
I downloaded java-bigquery repo and modified $/java-bigquery/samples/snippets/src/main/java/com/example/bigquery/Query.java as follows:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO(developer): Replace these variables before running the sample.
String projectId = "bigquery-public-data";
String datasetName = "samples";
String tableName = "natality";
String query =
"SELECT weight_pounds\n"
+ " FROM `"
+ projectId
+ "."
+ datasetName
+ "."
+ tableName
+ "`"
+ " LIMIT 1000000";
query(query);
}
public static void query(String query) {
try {
// Initialize client that will be used to send requests. This client only needs to be created
// once, and can be reused for multiple requests.
BigQuery bigquery = BigQueryOptions.getDefaultInstance().getService();
QueryJobConfiguration queryConfig = QueryJobConfiguration.newBuilder(query).setUseQueryCache(false).build();
TableResult results = bigquery.query(queryConfig);
System.out.println("total rows = " + results.getTotalRows());
results
.iterateAll()
.forEach(row -> row.forEach(val -> {}));
System.out.println("Query performed successfully.");
} catch (BigQueryException | InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Query not performed \n" + e.toString());
}
}
In above we are fetching 1 million rows from bigquery-public-data.samples.natality. Next run (from $/java-bigquery/samples/snippets):
$ mvn compile
$ gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
$ gcloud auth application-default login
and then run:
$ time mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass=com.example.bigquery.Query
...
total rows = 1000000
Query performed successfully.
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESS
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 19.915 s
[INFO] Finished at: 2022-06-23T18:06:25-07:00
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass=com.example.bigquery.Query 23.89s user 1.10s system 119% cpu 20.992 total
We see total time of 20.992s
Python
Begin by doing:
$ virtualenv myenv
$ source myenv/bin/activate
$ myenv/bin/pip install google-cloud-bigquery
$ gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
$ cd myenv
Create following python file test.py:
from google.cloud import bigquery
client = bigquery.Client()
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig(use_query_cache=False)
# Perform a query.
QUERY = (
'SELECT weight_pounds FROM `bigquery-public-data.samples.natality` '
'LIMIT 100000')
query_job = client.query(QUERY, job_config=job_config) # API request
rows = query_job.result() # Waits for query to finish
for row in rows:
pass
print("Got {} rows.".format(rows.total_rows))
Execute:
$ time python test.py
Got 1000000 rows.
python test.py 7.92s user 0.91s system 36% cpu 24.216 total
So a little worse than Java but nowhere as bad as the Python BQ connector that ships with Apache Beam and should not cause one to prefer Java over Python.
In both cases the total time includes the time to stream the data from BQ to my computer over my network. We read 1M records. Each record is a FLOAT64 or 8 bytes so total payload is 8MB.
>>> 8000.0/20.992
381.0975609756097
>>> 8000.0/24.216
330.3600925008259
How to get just the time spend in BigQuery?
It is possible to get just the time spend in BigQuery. This time is agnostic of the language one is using i.e., doesn’t matter if you use Java or Python. There are couple of ways you can do this.
Method 1
Retrieve the job details using below script. Make sure to change the Job ID. You can get the Job ID by viewing your request history in BQ on console.cloud.google.com. Look for the Personal History or Project History in BQ console.
#!/bin/bash
# Copyright 2019 Google LLC.
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
JOBID=XXX # CHANGE
access_token=$(gcloud auth application-default print-access-token)
PROJECT=$(gcloud config get-value project)
echo "$request"
curl --silent \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $access_token" \
-X GET \
"https://www.googleapis.com/bigquery/v2/projects/$PROJECT/jobs/${JOBID}"
This gives a wealth of information a subset of which is shown below
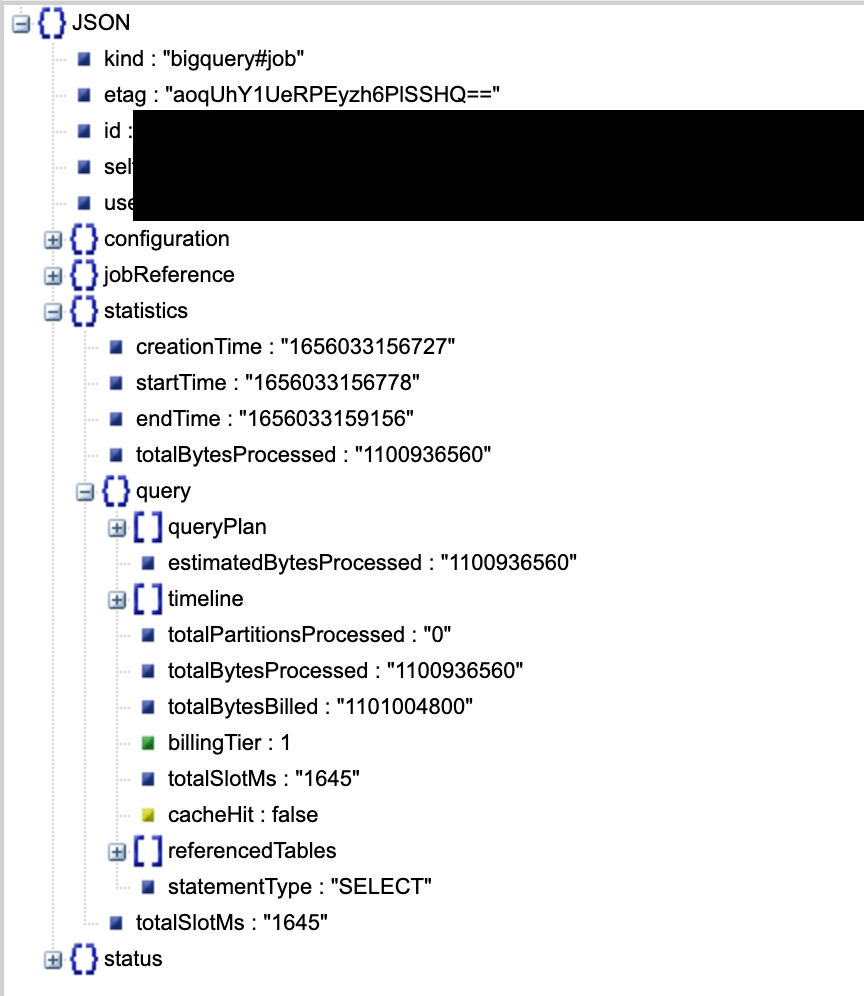
The total slot time is 1645ms.
Method 2
Run the query with cache enabled.
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig(use_query_cache=True)
In first run, it should give total time without any caching. In second run, results will be retrieved from the cache. The difference of two is the time spent in BigQuery. This is what I got:
(python-venv) python-venv ❯ time python test.py
Got 1000000 rows.
python test.py 7.96s user 0.96s system 35% cpu 25.240 total
(python-venv) python-venv ❯ time python test.py
Got 1000000 rows.
python test.py 7.93s user 0.86s system 40% cpu 21.867 total
A difference of about 3.3s
Method 3 – Use BigQueryWorkloadTester (Advanced)
Refer this. There are many issues though. Looks like the program is outdated. It won’t compile on latest version of Gradle and even if you got it to compile, it gave me runtime errors. Fixing it took the better half of a day. The runtime errors was because I was using a config.yaml under project root. In summary to use the tool:
- If you are on Gradle 7.x, you will need to edit the
build.gradlefiles to upgrade from6.xto7.x. This includes among other things:- replace
compilewithimplementation - replace
testCompilewithtestImplementation - replace
httpwithhttpsinrepositories - comment out
apply plugin: "maven"in thebuild.gradleunderpontemdirectory - add a
annotationProcessor group: 'com.google.auto.value', name: 'auto-value', version: '1.6.3'to get rid of error otherwise
- replace
- And after that note the program takes input a
config.yamland will always look for it undersrc/main/resources. Similarly if you are passing any query files, the program will look for them undersrc/main/resources - There should be one query per line in the query file. Thus, you cannot split a query into multiple lines.
Here is sample config.yaml
# The number of times a Workload will be executed in parallel.
# Our Concurrency Level limit is 50
concurrencyLevel: 1
# Whether to run several instances of the same Workload at different percentages of the provided
# Concurrency Level.
isRatioBasedBenchmark: true
# Which ratios of the concurrencyLevel to use with in a Ratio Based Benchmark.
# If no ratios are provided and Ratio Based Benchmark is used the Workload Execution will fail.
# Please remember that the concurrencyLevel limit is 50, the first ratio to surpass this limit will
# be swapped for 50 and all others will be ignored.
benchmarkRatios: [0.01, 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0]
# The folder where to save the results file.
outputFileFolder: /Users/xxx/pontem/BigQueryWorkloadTester/results
# The Workloads and their associated query files.
#
# If the Credentials file is empty the tool will attempt to load the default Credentials
# The Workload Tester expects the query file to contain one query per line.
# The Workload Tester can read queries from files via 'queryFiles' or you can produce a query / list
# of queries with 'queries'.
workloads:
- name: "Natality"
projectId: "xxx"
cloudCredentialsFile: ""
queryFiles:
# the program will look for natality.sql under src/main/resources
- natality.sql
#queries:
# - ""
outputFileName: natality.json
Here are results of running the program. There are two times reported by the program:
- Walltime: The time, in milliseconds, that it took for the query to be executed since we issued the BigQuery request until we received the response. Do note that
Walltimewill include the time for the network roundtrip and any scheduling / processing BigQuery may perform before running your query. - Runtime: The processing time, in milliseconds, that BigQuery took to execute your query.
This method gives us approx. 2.1s to execute the query.
